Charcot Foot
What is Charcot foot?
Charcot foot can result from complete or near-complete numbness in one or both feet or ankles. This condition causes the bones in the foot to become weak, making them prone to damage such as fractures and dislocation.
Because the foot is numb, pain from fractures or other traumas can go unnoticed, leading to additional damage from walking and standing.
As the bones continue to weaken, the joints of the foot can become dislocated or collapse, changing the foot’s shape. The resulting shape is referred to as rocker-bottom foot, since the arch extends down and out, creating a rocker-like appearance.
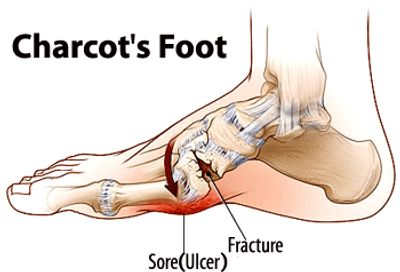
Charcot foot can also lead to the occurrence of sores, which are hard to heal.
If left untreated, Charcot foot can lead to severe deformity, disability, or amputation.
Charcot foot causes
Charcot foot occurs in people who have numbness in their feet and legs. This loss of sensation is the result of a type of nerve damage called peripheral neuropathy.
Charcot foot is most closely associated as a rare complication of diabetes, but peripheral neuropathy is associated with several conditions. These include:
- diabetes
- alcohol use disorder
- drug abuse
- leprosy
- syphilis
- syringomyelia
- polio
- infection, trauma, or damage in the peripheral nerves
- HIV
- Parkinson’s disease
- inflammatory conditions, such as sarcoidosis or psoriasis
Diagnosing Charcot foot
During stage one, Charcot foot may go undiagnosed since X-rays may not yet pick up on the damage starting to occur. For this reason, it’s important to let your doctor know if you have a medical condition that might result in Charcot foot.
In its later stages when it has progressed, imaging technologies such as X-rays and MRIs can be helpful.
In addition to analyzing your symptoms, your doctor will check for signs of neuropathy via a physical exam, a review of your medical history, and tests. These may include:
- Semmes-Weinstein 5.07/10 gram monofilament test, which analyzes sensitivity to pressure and touch in large nerve fibers
- pinprick test, which assesses ability to feel pain
- neurometer test, which identifies peripheral nerve dysfunction such as diabetic neuropathy
Your doctor will also test your tendon reflexes and analyze the muscle tone and strength in your leg and foot.
Charcot foot treatments
Treatment for Charcot foot in its early stage is geared towards reducing swelling and heat in the area, as well as stabilizing the foot by keeping it immobile. It’s important to eliminate any weight or pressure on the foot to stop additional damage from being done. This is sometimes referred to as off-loading.
You should regularly see a doctor, who will monitor your condition and progress. If only one foot is affected, your other foot will be monitored for symptoms during this time.
Once your foot has healed, you may be fitted for therapeutic shoes or diabetic footwear to reduce or eliminate your chances of getting Charcot foot in the future.
Charcot foot surgery
Your doctor may recommend surgery if your foot has become significantly unstable or if it cannot be braced or supported in any way. You may also require surgery if you have a sore or ulcer that doesn’t heal. Surgical techniques include:
- Reconstructive osteotomy. Also known as realignment bone surgery, this procedure shortens or lengthens a bone in the foot or ankle to alter its alignment and ability to support the joints. A surgeon shortens the bone by cutting it or lengthens the bone by adding a wedge of bone to it.
- Ankle fusion. This procedure uses screws, rods, or plates to lock the ankle joint, prohibiting motion.
- Exostectomy. This is removal of plantar prominences, which might cause ulcers to form.
- Amputation and prosthetic fitting. The foot or portion of the foot is removed, followed by fitting for a prosthetic device.
Copyright © 2024 Central Texas Foot & Ankle Centers - All Rights Reserved.